国际化
国际化(Internationalization,简写为 I18n),是指在设计和开发产品、应用程序时,对其进行本地化,以适应不同的文化、地区或语言的目标用户。你可以使用 i18next 等 i18n 库实现国际化,为用户提供易于访问的体验。
Intl API
Intl 对象是 ECMAScript 国际化 API 的一个命名空间,提供了一组处理国际化与本地化的方法。通过 Intl API,能够处理数字、日期和时间等相关问题,比如数字格式化、日期和时间格式化。
目前在 Lynx 中 Intl API 尚未实现,并将在后续版本中支持。如果你需要使用在 Lynx 中使用 Intl API,你可以安装对应的 Polyfill,例如 @formatjs/intl-numberformat
、@formatjs/intl-datetimeformat、intl-pluralrules 等。
使用 i18next
i18next 是一个 JavaScript 国际化框架,在 ReactLynx 中使用它有以下优点:
- 简洁:
i18next 提供了简单易用的 API,让在 ReactLynx 中实现国际化变得更加简单
- 按需加载:支持按需加载语言资源,减少首屏加载时间
- 广泛支持:兼容多种格式和后端,允许与不同的翻译存储解决方�案(如 JSON 文件、远程 API 等)轻松集成。
- 支持缓存:内置缓存机制加快语言资源的加载速度,提升用户体验。
- 丰富的社区支持:拥有庞大的社区和丰富的插件,满足多样化的国际化需求。
- 可靠性:在众多项目中得到验证,提供稳定性和可靠性。
- 热重载:语言资源的更改可以立即生效,无需重新发布应用。
安装
你需要安装 i18next 作为依赖:
npm install i18next@^23.16.8
创建第一个文案翻译
假设我们有如下的文案资源:
创建翻译函数只需要以下三个步骤:
- 引入文案资源
./locales/en.json
- 使用
createInstance() 函数创建 i18next 实例
- 用引入的文案资源初始化 i18n 实例
src/i18n.ts
import i18next from 'i18next';
import type { i18n } from 'i18next';
import enTranslation from './locales/en.json';
const localI18nInstance: i18n = i18next.createInstance();
localI18nInstance.init({
lng: 'en',
// The default JSON format needs `Intl.PluralRules` API, which is currently unavailable in Lynx.
compatibilityJSON: 'v3',
resources: {
en: {
translation: enTranslation, // `translation` is the default namespace
},
},
});
export { localI18nInstance as i18n };
TIP
如果你在 TypeScript 文件中引入 *.json, 你需要在 tsconfig.json 文件中设置 compilerOptions.resolveJsonModule 选项为 true。
tsconfig.json
{
"compilerOptions": {
"resolveJsonModule": true
}
}
接下来,可以直接使用 i18n.t 函数来进行文案翻译:
src/App.tsx
import { useEffect } from '@lynx-js/react';
import { i18n } from './i18n.js';
export function App() {
useEffect(() => {
console.log(`Hello, ReactLynx x i18next!`);
}, []);
return (
<view>
<text>Hello, {i18n.t('world')}</text>
</view>
);
}
同步加载文案资源
在真实的项目中,通常有多个不同语言的文案资源。
你可以使用 import.meta.webpackContext API 来一次性将他们全部引入:
import one-by-one
// Static-imported locales that can be shown at first screen
import enTranslation from './locales/en.json';
import zhTranslation from './locales/zh.json';
import itTranslation from './locales/it.json';
import jpTranslation from './locales/jp.json';
import deTranslation from './locales/de.json';
import esTranslation from './locales/es.json';
import frTranslation from './locales/fr.json';
import idTranslation from './locales/id.json';
import ptTranslation from './locales/pt.json';
import.meta.webpackContext
const localesContext = import.meta.webpackContext('./locales', {
recursive: false,
regExp: /\.json$/,
});
const enTranslation = localesContext('en.json');
这些资源也可以被添加到 i18next.init() 中来让首屏渲染中的文案得到翻译:
src/i18n.ts
import i18next from 'i18next';
import type { i18n } from 'i18next';
// Localizations imported statically, available at the initial screen
const localesContext = import.meta.webpackContext('./locales', {
recursive: false,
regExp: /\.json$/,
});
const localI18nInstance: i18n = i18next.createInstance();
localI18nInstance.init({
lng: 'en',
// The default JSON format needs Intl.PluralRules API, which is currently unavailable in Lynx.
compatibilityJSON: 'v3',
// Add all statically imported localizations to i18next resources.
resources: Object.fromEntries(
localesContext.keys().map((key) => [
key.match(/\/([^/]+)\.json$/)?.[1] || key,
{
translation: localesContext(key) as Record<string, string>,
},
]),
),
});
export { localI18nInstance as i18n };
异步��按需加载文案资源
同步加载资源会使得全部的文案资源都打包在产物中,导致首屏加载性能较差。
我们也可以通过 import() 来异步、按需引入文案资源。
首先需要安装 i18next-resources-to-backend 作为依赖:
npm install i18next-resources-to-backend
接下来在 src/i18n.ts 中添加下面的代码:
src/i18n.ts
import i18next from 'i18next';
import type { i18n } from 'i18next';
import resourcesToBackend from 'i18next-resources-to-backend';
// Localizations imported statically, available at the initial screen
const localesContext = import.meta.webpackContext('./locales', {
recursive: false,
regExp: /(en|zh)\.json$/,
});
const localI18nInstance: i18n = i18next.createInstance();
// We can only loading resources on a background thread
if (__JS__) {
localI18nInstance.use(
// See: https://www.i18next.com/how-to/add-or-load-translations#lazy-load-in-memory-translations
resourcesToBackend(
(language: string) =>
// Dynamic-imported locales can be used with `i18n.loadLanguages`
import(`./locales/${language}.json`),
),
);
}
localI18nInstance.init({
lng: 'en',
// The default JSON format needs Intl.PluralRules API, which is currently unavailable in Lynx.
compatibilityJSON: 'v3',
// Add all statically imported localizations to i18next resources.
resources: Object.fromEntries(
localesContext.keys().map((key) => [
key.match(/\/([^/]+)\.json$/)?.[1] || key,
{
translation: localesContext(key) as Record<string, string>,
},
]),
),
partialBundledLanguages: true,
});
export { localI18nInstance as i18n };
在上面的例子中
- 一个
i18next 的中间件 i18next-resources-to-backend 在后台线程中被添加到 localI18nInstance.use 当中
- 文案资源可以被异步按需加载(其中的部分,如
zh, en 依然同步加载)
在产物中,可以看到生成了多个 JavaScript 文件,其中包含了文案资源:
src_locales_it-IT_json.js
'use strict';
exports.ids = ['src_locales_it-IT_json'];
exports.modules = {
'./src/locales/it-IT.json': function (module) {
module.exports = JSON.parse('{"world": "Mondo"}');
},
};
src_locales_ja-JP_json.js
'use strict';
exports.ids = ['src_locales_ja-JP_json'];
exports.modules = {
'./src/locales/ja-JP.json': function (module) {
module.exports = JSON.parse('{"world": "世界"}');
},
};
你可能还会注意到这两个没有被加载,这就是为什么它被称为按需加载,对资源的请求仅在需要时才会发送。
💡 为什么没有为 src/locales/en.json 生成单独的 JavaScript 文件?
切换语言
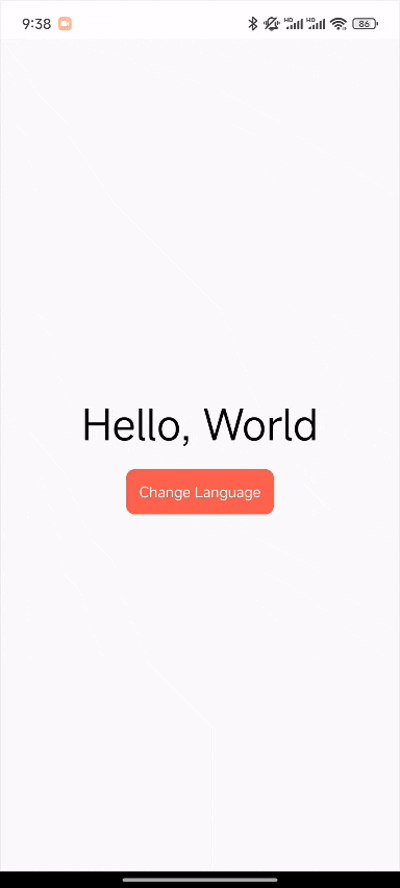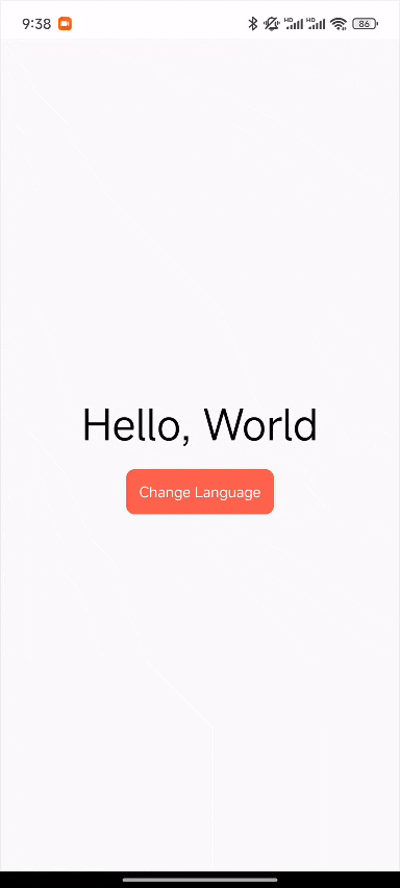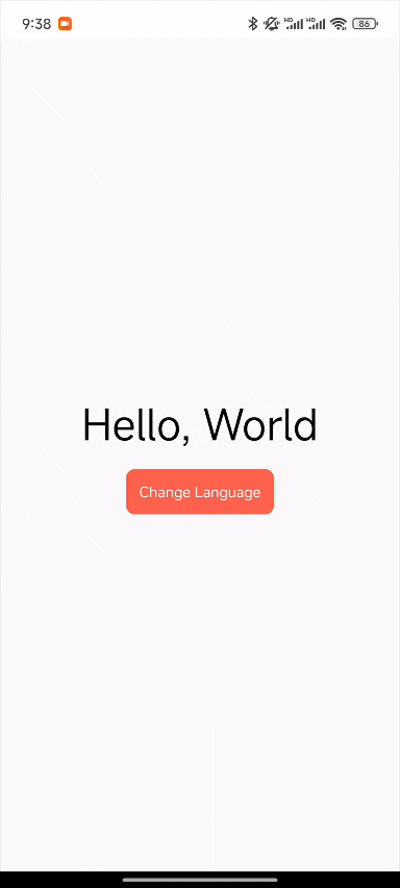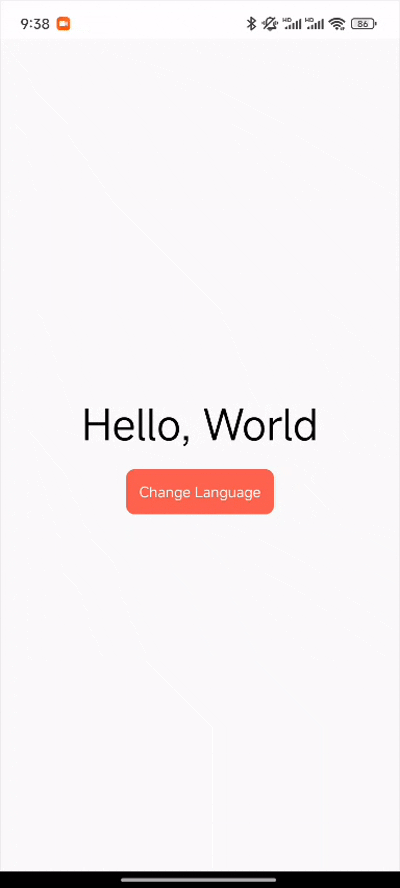
调用 i18next.changeLanguage API 可以在不同语言间进行切换:
src/App.tsx
import { useEffect, useState } from '@lynx-js/react';
import { i18n } from './i18n.js';
export function App() {
const [locale, setLocale] = useState('en');
useEffect(() => {
console.log('Hello, ReactLynx3 x i18next!');
}, []);
const getNextLocale = (locale: string) => {
// mock locales
const locales = ["en", "zh-CN"];
const index = locales.indexOf(locale);
return locales[(index + 1) % locales.length];
};
return (
<view>
<text style={{ color: 'red' }}>Current locale: {locale}</text>
<text
bindtap={async () => {
const nextLocale = getNextLocale(locale);
await i18n.changeLanguage(nextLocale);
setLocale(nextLocale);
}}
>
Tap to change locale
</text>
<text>Hello, {i18n.t('world')}</text>
</view>
);
}