Internationalization
Internationalization (i18n) refers to the design and development of products and applications to enable localization, making them suitable for users from different cultures, regions, or languages. You can use i18n libraries like i18next to achieve internationalization and provide an accessible experience for users.
Intl API
The Intl object is a namespace for the ECMAScript Internationalization API, providing a set of methods for handling internationalization and localization. With the Intl API, you can handle issues related to numbers, dates, and times, such as number formatting and date and time formatting.
Currently, the Intl API is not implemented in Lynx but will be supported in future versions. If you need to use the Intl API in Lynx, you can install the corresponding polyfills, such as @formatjs/intl-numberformat, @formatjs/intl-datetimeformat, and intl-pluralrules.
Using i18next
i18next is an internationalization-framework written in and for JavaScript. Using it in ReactLynx gives you:
- Simplicity:
i18next provides an easy-to-use API, making it simple to implement internationalization in ReactLynx applications.
- Dynamic Loading: Supports on-demand loading of language resources, reducing initial load time.
- Wide Support: Compatible with various formats and backends, allowing easy integration with different translation storage solutions such as JSON files, remote APIs, etc.
- Caching: Built-in caching mechanism speeds up the loading of language resources, enhancing user experience.
- Rich Community Support: A vast community and a wealth of plugins available to meet diverse internationalization needs.
- Reliability: Proven in numerous projects, offering stability and reliability.
- Hot Reloading: Changes to language resources can take effect immediately without needing to republish the application.
Installation
You need to install the i18next package:
npm install i18next@^23.16.8
TIP
Since the version 24.0.0+ of i18next, the running environment is required to have the Intl.pluralRules API. However, this implementation is currently not available on Lynx.
This means that you need to:
- Use v23 and must enable
compatibilityJSON: 'v3'.
- Use v24 and need to polyfill the
Intl.PluralRules API.
Create the first translation
Imagine we have a locale file src/locales/en.json like this:
Creating the translation function is as simple as these 3 steps:
- Import the locale JSON file
./locales/en.json.
- Create an i18next instance with the
createInstance() function.
- Initialize the i18n with the locale resource.
src/i18n.ts
import i18next from 'i18next';
import type { i18n } from 'i18next';
import enTranslation from './locales/en.json';
const localI18nInstance: i18n = i18next.createInstance();
localI18nInstance.init({
lng: 'en',
// The default JSON format needs `Intl.PluralRules` API, which is currently unavailable in Lynx.
compatibilityJSON: 'v3',
resources: {
en: {
translation: enTranslation, // `translation` is the default namespace
},
},
});
export { localI18nInstance as i18n };
TIP
If you import *.json in TypeScript file, you may need to set compilerOptions.resolveJsonModule to true in your tsconfig.json file.
tsconfig.json
{
"compilerOptions": {
"resolveJsonModule": true
}
}
Then, the i18n.t function can be used for translations:
src/App.tsx
import { useEffect } from '@lynx-js/react';
import { i18n } from './i18n.js';
export function App() {
useEffect(() => {
console.log(`Hello, ReactLynx x i18next!`);
}, []);
return (
<view>
<text>Hello, {i18n.t('world')}</text>
</view>
);
}
Load resources synchronously
In a real world project, there are usually multiple resource files for different languages.
Instead of static import them one-by-one,
you may use the import.meta.webpackContext API of Rspack to statically import all the JSON files.
import one-by-one
// Static-imported locales that can be shown at first screen
import enTranslation from './locales/en.json';
import zhTranslation from './locales/zh.json';
import itTranslation from './locales/it.json';
import jpTranslation from './locales/jp.json';
import deTranslation from './locales/de.json';
import esTranslation from './locales/es.json';
import frTranslation from './locales/fr.json';
import idTranslation from './locales/id.json';
import ptTranslation from './locales/pt.json';
import.meta.webpackContext
const localesContext = import.meta.webpackContext('./locales', {
recursive: false,
regExp: /\.json$/,
});
const enTranslation = localesContext('en.json');
These resources can be added to i18next.init() to make translation work at the first screen.
src/i18n.ts
import i18next from 'i18next';
import type { i18n } from 'i18next';
// Localizations imported statically, available at the initial screen
const localesContext = import.meta.webpackContext('./locales', {
recursive: false,
regExp: /\.json$/,
});
const localI18nInstance: i18n = i18next.createInstance();
localI18nInstance.init({
lng: 'en',
// The default JSON format needs Intl.PluralRules API, which is currently unavailable in Lynx.
compatibilityJSON: 'v3',
// Add all statically imported localizations to i18next resources.
resources: Object.fromEntries(
localesContext.keys().map((key) => [
key.match(/\/([^/]+)\.json$/)?.[1] || key,
{
translation: localesContext(key) as Record<string, string>,
},
]),
),
});
export { localI18nInstance as i18n };
Load resources asynchronously and lazily
Instead of bundling all the locales, we can use dynamic imports (import()) to load the locales lazily and asynchronously.
You need to install the i18next-resources-to-backend package:
npm install i18next-resources-to-backend
Then add the following code to src/i18n.ts:
src/i18n.ts
import i18next from 'i18next';
import type { i18n } from 'i18next';
import resourcesToBackend from 'i18next-resources-to-backend';
// Localizations imported statically, available at the initial screen
const localesContext = import.meta.webpackContext('./locales', {
recursive: false,
regExp: /(en|zh)\.json$/,
});
const localI18nInstance: i18n = i18next.createInstance();
// We can only loading resources on a background thread
if (__JS__) {
localI18nInstance.use(
// See: https://www.i18next.com/how-to/add-or-load-translations#lazy-load-in-memory-translations
resourcesToBackend(
(language: string) =>
// Dynamic-imported locales can be used with `i18n.loadLanguages`
import(`./locales/${language}.json`),
),
);
}
localI18nInstance.init({
lng: 'en',
// The default JSON format needs Intl.PluralRules API, which is currently unavailable in Lynx.
compatibilityJSON: 'v3',
// Add all statically imported localizations to i18next resources.
resources: Object.fromEntries(
localesContext.keys().map((key) => [
key.match(/\/([^/]+)\.json$/)?.[1] || key,
{
translation: localesContext(key) as Record<string, string>,
},
]),
),
partialBundledLanguages: true,
});
export { localI18nInstance as i18n };
-
An i18next backend i18next-resources-to-backend has been added to the background thread with localI18nInstance.use.
-
The languages can be loaded asynchronously (with some of them being loaded synchronously).
You will see two async JS chunks are created in the output:
src_locales_it-IT_json.js
'use strict';
exports.ids = ['src_locales_it-IT_json'];
exports.modules = {
'./src/locales/it-IT.json': function (module) {
module.exports = JSON.parse('{"world": "Mondo"}');
},
};
src_locales_ja-JP_json.js
'use strict';
exports.ids = ['src_locales_ja-JP_json'];
exports.modules = {
'./src/locales/ja-JP.json': function (module) {
module.exports = JSON.parse('{"world": "世界"}');
},
};
💡 Why is there no async chunk generated by src/locales/en.json
This is because this module is already included in the main chunk. Webpack/Rspack will remove it automatically.
See: optimization.removeAvailableModules and optimization.removeEmptyChunks for details.
You may also see that these two chunks are not loaded. This is why it is called lazily. The request to the resources is only sent when needed.
You may also see that these two chunks are not loaded. This is why it is called lazily. The request to the resources is only sent when needed.
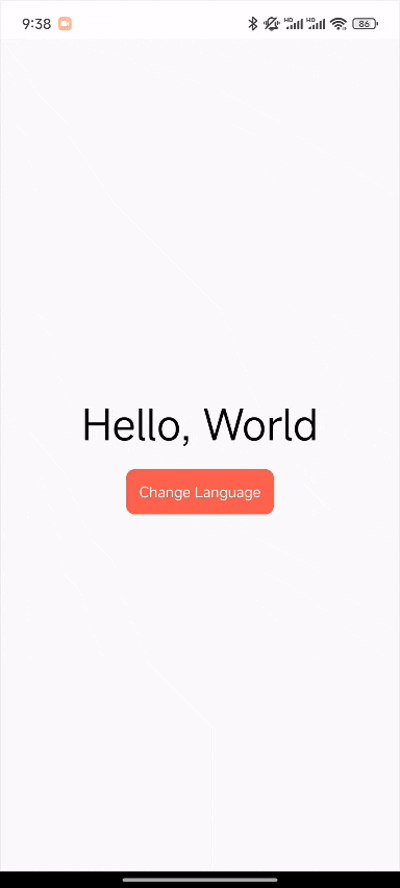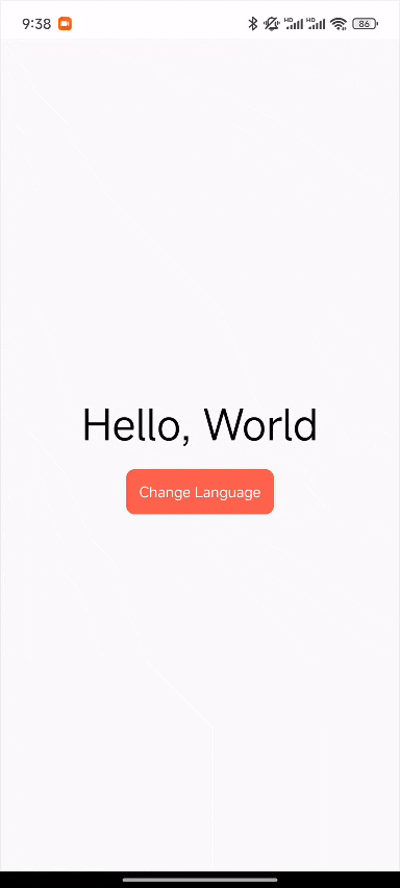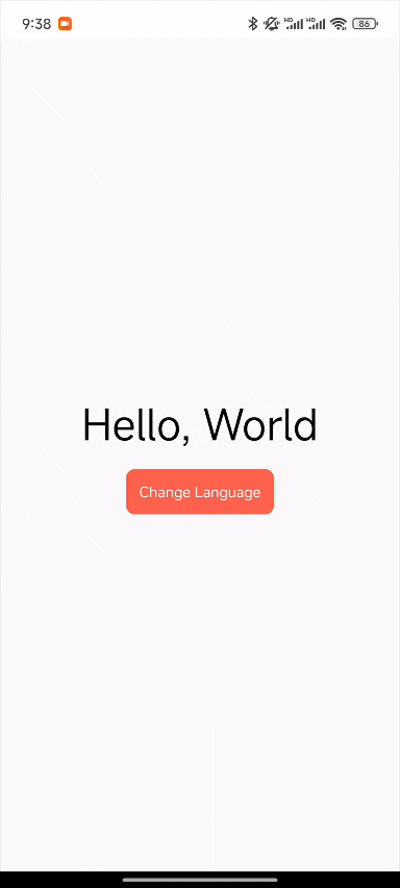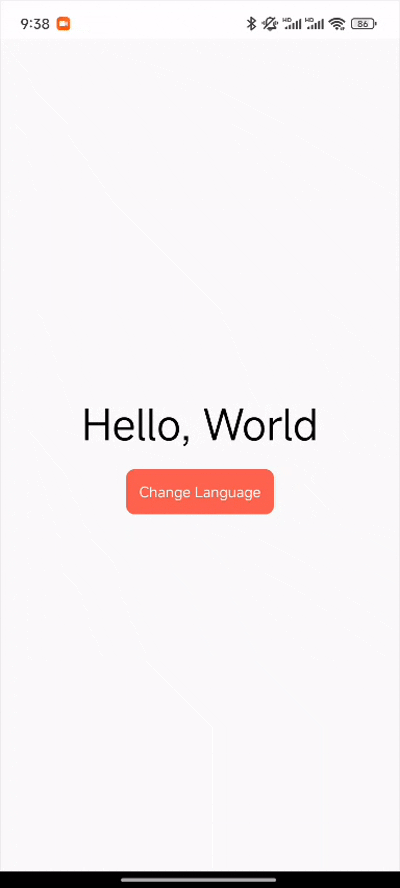
Change between languages
The i18next.changeLanguage API can be used for changing between languages.
src/App.tsx
import { useEffect, useState } from '@lynx-js/react';
import { i18n } from './i18n.js';
export function App() {
const [locale, setLocale] = useState('en');
useEffect(() => {
console.log('Hello, ReactLynx3 x i18next!');
}, []);
const getNextLocale = (locale: string) => {
// mock locales
const locales = ["en", "zh-CN"];
const index = locales.indexOf(locale);
return locales[(index + 1) % locales.length];
};
return (
<view>
<text style={{ color: 'red' }}>Current locale: {locale}</text>
<text
bindtap={async () => {
const nextLocale = getNextLocale(locale);
await i18n.changeLanguage(nextLocale);
setLocale(nextLocale);
}}
>
Tap to change locale
</text>
<text>Hello, {i18n.t('world')}</text>
</view>
);
}