Relative Layout no Web
If you want a layout that allows easily control the relative position between the parent and children or between the sibling elements without using complex hierarchical structure, relative layout (inspired by relative Layout in Android) is the best choice. While using grid, flexible box, and linear layouts, it's challenging to achieve a design that includes numerous relative positions using only a few styles.
Relative layout is a layout that displays children in relative positions, where each view's position can be specified relative to sibling elements (for example, to the left or below another view) or relative to the parent's area (e.g., align at bottom, left or center). For the supported properties, please refer to the Reference section.
How to Build a Relative Layout?
In the scenario described below, where the "user name" and "description" have a positional relationship, and the "user name" also aligns with the "avatar" on the right. What's more, the "follow", "close", "user" also have corresponding relationships with each other. The dashed lines and arrows in the image below are to indicate their positional relationship.
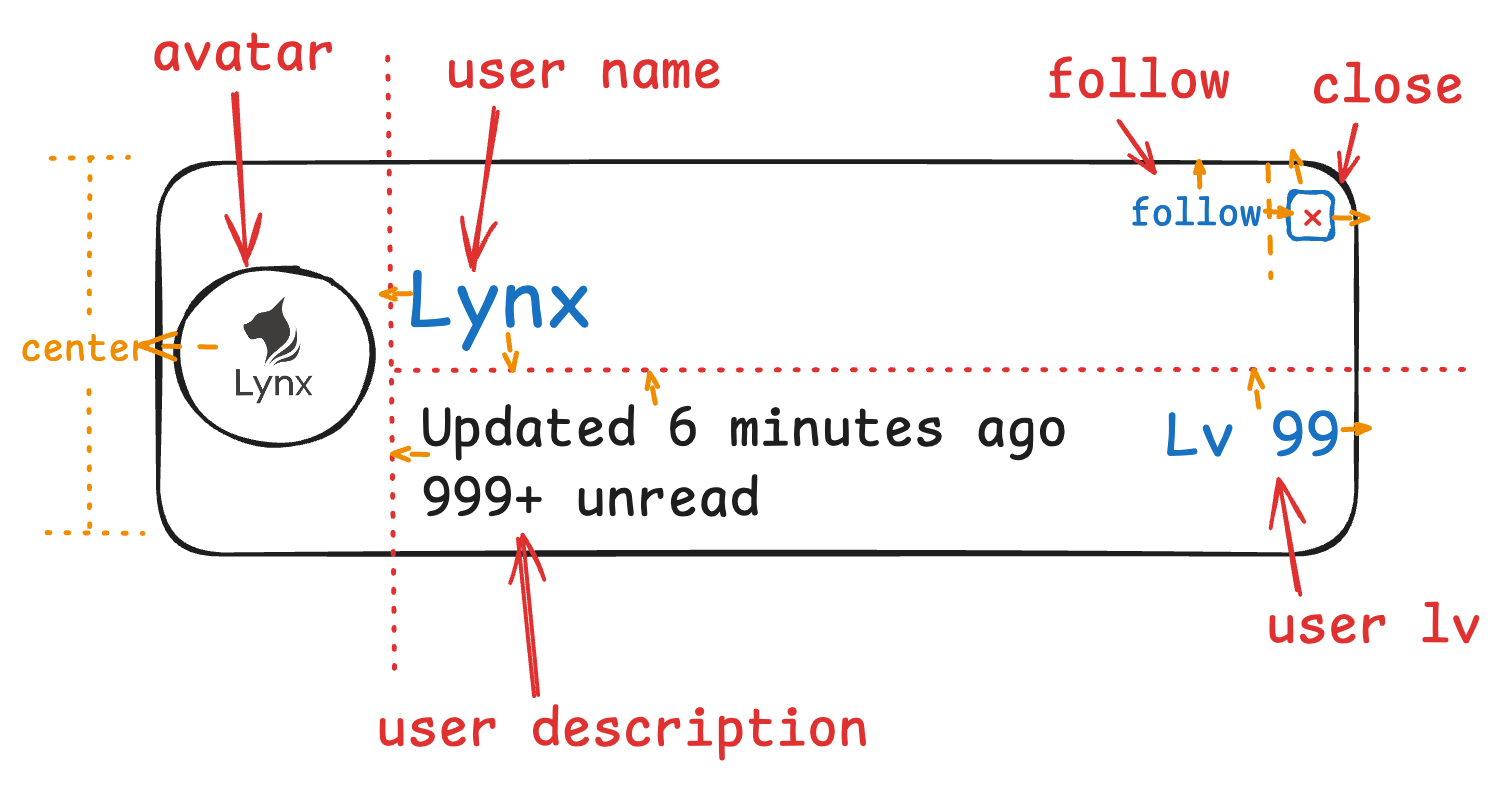
Let's implement the above diagram using the relative layout in following steps:
Step 1: Apply display: relative
You can apply display: relative to the parent element where you want the relative layout.
Step 2: Set ID for Children
Assign a unique relative-id (integer, not 0) for each child in the relative layout. This step is to better identify each element.
Step 3: Set Edge Alignment Properties
Use these edge alignment properties to specify alignment of the element with its parent or sibling's edge. For instance, relative-align-top ensures the element aligns with the top edge of the designated parent or sibling id.
Physical Properties
Logical Properties
Step 4: Set Relative Position Properties
Define relative positioning of the current element to its sibling elements using these properties. As an example, relative-left-of arranges the current element to the left of the designated sibling, closely aligning right edge with the sibling's left edge.
Physical Properties
Logical Properties
Step 5: Set Center Property
Use relative-center declare how the current children element is centered in the container. By setting vertical to achieve vertical centering, setting horizontal to achieve horizontal centering, or setting both to simultaneously achieve both vertical and horizontal centering.
Example
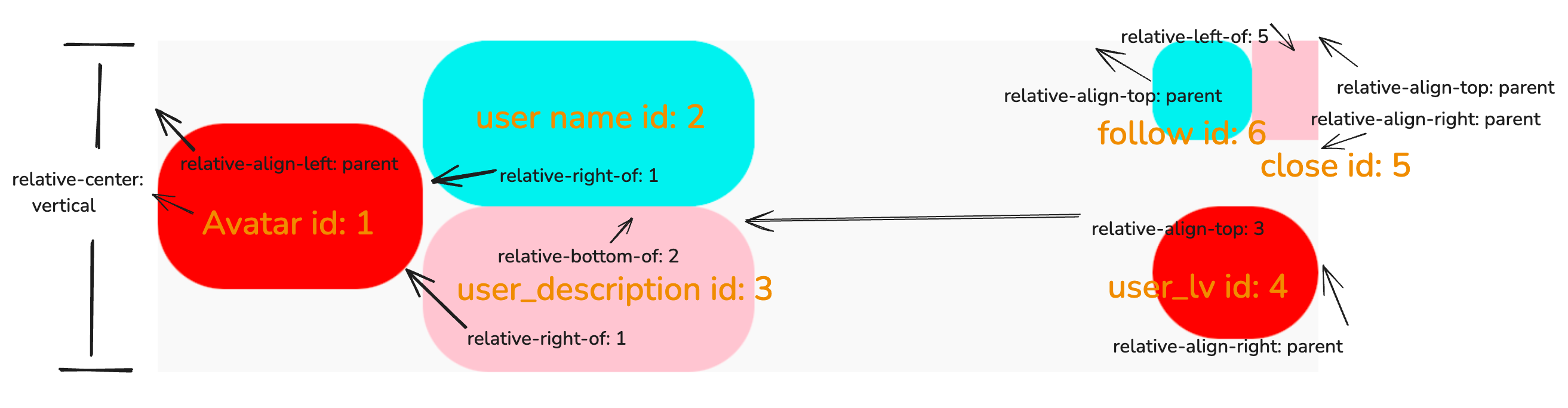
In this example, the container's width is fixed, while its height adjusts to its content. To incorporate gaps between elements, use margin.

-
Best Practices
Reasonable use of the relative layout can offer developers a convenient and efficient layout experience. Therefore, it is strongly recommended that developers follow the following points when developing.
- Parent container positioning can be used freely without affecting performance.
- When using the positioning between sibling elements, it is recommended to enable the
relative-layout-once(default enabled) style, and the sibling element will only rely on upwards. - Avoid circular dependencies where 'a' depends on 'b' for its horizontal width, and 'b' depends on 'a' for its vertical width, as this can severely impact performance.
- Please do not have unresolved circular dependencies, which cannot get the correct layout result.
- Try to use logical attributes, inline-start and inline-end, to facilitate page internationalization support.
Reference
-
Relative Id
-
Edge Alignment Properties
Physical Properties
Logical Properties
-
Relative Position Properties
Physical Properties
Logical Properties
-
Center Property
-
Layout Optimization Property