#使用 Trace API
Lynx Trace 支持你在代码中添加自定义 Trace 事件,帮助你追踪特定操作或业务流程。这对于分析自定义业务逻辑、统计耗时或标记应用中的关键节点非常有用。
- 对于前端开发者:你可能想要测量某个 Hook 或组件生命周期方法的执行时间,以了解渲染延迟或副作用的耗时。例如,跟踪 useEffect Hook 执行的时长;
- 对于 Android/iOS 开发者:你可能想要分析加载 Lynx Bundle、解析资源或执行某个 NativeModule 调用所花费的时间。自定义埋点事件帮助你精准定位复杂流程中的性能瓶颈;
通过添加自定义 Trace 事件,你可以将代码中不透明的部分转化为 Lynx Trace 时间线中可视且可度量的区间,从而实现精准的性能调优。
#如何使用
#Slice 事件
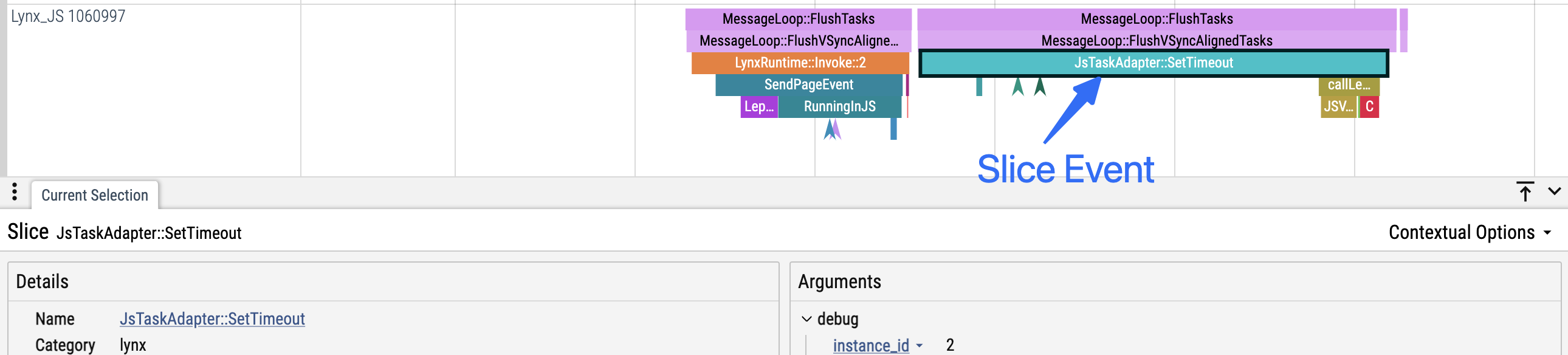
- 定义:Slice 事件具有开始和结束时间戳,表示一个持续的区间。
- 嵌套:在同一线程上,Slice 事件可以像调用栈一样嵌套。
- 例如,如果事件 B 在事件 A 开始后且 A 结束前开始,则 B 被视为 A 的子事件,并会在 Trace UI 中以��嵌套的形式显示在 A 之下。
- 适用场景:适合用于分析关心执行耗时的代码片段。
TIP
子事件必须始终在其父事件结束前结束(即 B 必须在 A 之前结束)
// 基础用法
- (void)measure {
[LynxTraceEvent beginSection:@"render" withName:@"measure"]; // 'measure' slice 开始
// ... 你的代码 ...
[LynxTraceEvent endSection:@"render" withName:@"measure"]; // 'measure' slice 结束
}
// 带自定义参数
- (void)draw {
[LynxTraceEvent beginSection:@"render" withName:@"draw-image" debugInfo:@{@"component": @"Image", @"size": @"large"}];
// ... 你的代码 ...
[LynxTraceEvent endSection:@"render" withName:@"draw-image"];
}#Instant 事件
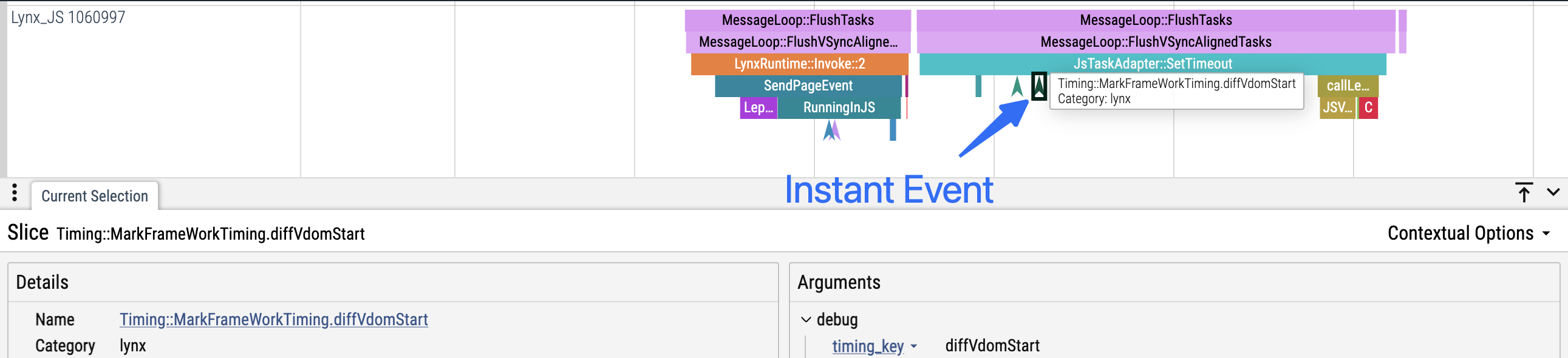
- 定义:Instant 事件只有一个时间戳,没有持续时间。
- 适用场景:适用于标记代码中的重要时刻或节点(如状态变更、跨线程/异步边界等)。
// 基础用法
- (void)requestBegin {
// ...
[LynxTraceEvent instant:@"network" withName:@"request-begin"];
// ...
}
// 带自定义参数
- (void)requestFinished {
// ...
[LynxTraceEvent instant:@"network" withName:@"request-finished" debugInfo:@{@"url": @"https://example.com", @"method": @"GET"}];
// ...
}#最佳实践
#Begin/End 必须在同一线程且成对出现
- 每个
beginSection必须有一个对应的endSection,且这两个调用必须发生在同一线程。 - 不要因为异常或提前 return 而导致
endSection未被调用。
#错误示例
// 异常导致 endSection 未被调用
- (void)measureWithError:(BOOL)shouldThrow {
[LynxTraceEvent beginSection:@"measure"];
// ...
@throw [NSException exceptionWithName:@"TestException" reason:@"Error occurred" userInfo:nil];
// 异常导致 endSection 未被调用
[LynxTraceEvent endSection:@"measure"];
}
// 提前 return 导致 endSection 未被调用
- (void)measureWithFastExit:(BOOL)fastExit {
[LynxTraceEvent beginSection:@"measure"];
// 直接返回,endSection 未被调用
if (fastExit) return;
// ...
[LynxTraceEvent endSection:@"measure"];
}
// 跨线程调用导致 begin/end 不匹配
[LynxTraceEvent beginSection:@"background-task"];
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_global_queue(DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_DEFAULT, 0), ^{
// ...
[LynxTraceEvent endSection:@"background-task"]; // 错误:不在同一线程
});#正确示例
- (void)measureWithError:(BOOL)shouldThrow {
@try {
LynxTraceEvent beginSection:@"measure"];
// ...
@throw [NSException exceptionWithName:@"TestException" reason:@"Error occurred" userInfo:nil];
}
@finally {
// 异常安全,确保 endSection 一定被调用
[LynxTraceEvent endSection:@"measure"];
}
}
- (void)measureWithFastExit:(BOOL)fastExit {
[LynxTraceEvent beginSection:@"measure"];
if (fastExit) {
// 提前 return 安全示例
[LynxTraceEvent endSection:@"measure"];
return;
}
// ...
[LynxTraceEvent endSection:@"measure"];
}
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_global_queue(DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_DEFAULT, 0), ^{
// 线程安全示例:begin/end 在同一线程
[LynxTraceEvent beginSection:@"background-task"];
// ...
[LynxTraceEvent endSection:@"background-task"];
});#不要跨异步边界使用 Slice 事件
- �不要在异步边界(如定时器、回调)之间使用
beginSection/endSection。 - Slice 事件要求开始和结束必须在同一个同步上下文中。
- 如果需要追踪异步边界两侧,请使用 Instant 事件。
#错误示例
// 定时器/回调
[LynxTraceEvent beginSection:@"async-function"];
dispatch_after(dispatch_time(DISPATCH_TIME_NOW, time), dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
// ...
[LynxTraceEvent endSection:@"async-function"];
});
// 异步任务
[LynxTraceEvent beginSection:@"await-task"];
[someAsyncFunction waitUntilFinished];
[LynxTraceEvent endSection:@"await-task"];#正确示例
// 定时器/回调:在回调内部成对使用
dispatch_after(dispatch_time(DISPATCH_TIME_NOW, time), dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
[LynxTraceEvent beginSection:@"async-function"];
// ...
[LynxTraceEvent endSection:@"async-function"];
});
// 异步任务:使用即时事件
[LynxTraceEvent instant:@"async-task" withName:@"start"];
[someAsyncFunction waitUntilFinished];
[LynxTraceEvent instant:@"async-task" withName:@"end"];#Slice 事件

- 定义:Slice 事件具有开始和结束时间戳,表示一个持续的区间。
- 嵌套:在同一线程上,Slice 事件可以像调用栈一样嵌套。
- 例如,如果事件 B 在事件 A 开始后且 A 结束前开始,则 B 被视为 A 的子事件,并会在 Trace UI 中以嵌套的形式显示在 A 之下。
- 适用场景:适合用于分析关心执行耗时的代码片段。
TIP
子事件必须始终在其父事件结束前结束(即 B 必须在 A 之前结束)
// 基础用法
void measure() {
TraceEvent.beginSection("render", "measure");
// ... 你的代码 ...
TraceEvent.endSection("render", "measure");
}
// 带自定义参数
void draw() {
Map<String, String> args = new HashMap<>();
args.put("component", "Image");
args.put("size", "large");
TraceEvent.beginSection("render", "draw-image", args);
// ... 你的代码 ...
TraceEvent.endSection("render", "draw-image");
}#Instant 事件

- 定义:Instant 事件只有一个时间戳,没有持续时间。
- 适用场景:适用于标记代码中的重要时刻或节点(如状态变更、跨线程/异步边界等)。
// 基本用法
void requestBegin() {
// ...
TraceEvent.instant("network", "request-begin");
// ...
}
// 带自定义参数
void requestFinished() {
// ...
Map<String, String> args = new HashMap<>();
args.put("url", "https://example.com");
args.put("method", "GET");
TraceEvent.instant("network", "request-finished", args);
//...
}#最佳实践
#Begin/End 必须在同一线程且成对出现
- 每个
beginSection必须有一个对应的endSection,且这两个调用��必须发生在同一线程。 - 不要因为异常或提前 return 而导致
endSection未被调用。
#错误示例
public void measure() throws Exception {
TraceEvent.beginSection("measure");
// ...
exceptionFunction(); // 可能抛出异常
// 异常导致 endSection 未被调用
TraceEvent.endSection("measure");
}
public void measure(boolean fastExit) {
TraceEvent.beginSection("measure");
// 提前 return 导致 endSection 未被调用
if (fastExit) return;
// ...
TraceEvent.endSection("measure");
}
// 跨线程:begin/end 不在同一线程
TraceEvent.beginSection("background-task");
new Thread(() -> {
// ...
TraceEvent.endSection("background-task");
}).start();#正确示例
public void measure() throws Exception {
try {
TraceEvent.beginSection("measure");
// ...
exceptionFunction();
} finally {
// 异常安全
TraceEvent.endSection("measure");
}
}
public void measure() {
TraceEvent.beginSection("measure");
if (fastExit) {
// 提前 return 安全
TraceEvent.endSection("measure");
return;
}
// ...
TraceEvent.endSection("measure");
}
new Thread(() -> {
// 线程安全:begin/end 在同一线程
TraceEvent.beginSection("background-task");
// ...
TraceEvent.endSection("background-task");
}).start();#不要跨异步边界使用 Slice 事件
- 不要在异步边界(如定时器、回调)之间使用
beginSection/endSection。 - Slice 事件要求开始和结束必须在同一个同步上下文中。
- 如果需要追踪异步边界两侧,请使用 Instant 事件。
#错误示例
// 定时器/回调
TraceEvent.beginSection("async-function");
new Handler().postDelayed(() -> {
// ...
TraceEvent.endSection("async-function");
}, 3000);
// 异步任务
TraceEvent.beginSection("await-task");
someAsyncFunction().get(); // 假设这是异步等待
TraceEvent.endSection("await-task");#正确示例
// 定时器/回调:在回调内部成对使用
new Handler().postDelayed(() -> {
TraceEvent.beginSection("async-function");
// ...
TraceEvent.endSection("async-function");
}, 3000);
// 异步任务:使用即时事件
TraceEvent.instant("async-task", "async-task-start");
someAsyncFunction().get();
TraceEvent.instant("async-task", "async-task-end");#Slice 事件

- 定义:Slice 事件具有开始和结束时间戳,表示一个持续的区间。
- 嵌套:在同一线程上,Slice 事件可以像调用栈一样嵌套。
- 例如,如果事件 B 在事件 A 开始后且 A 结束前开始,则 B 被视为 A 的子事件,并会在 Trace UI 中以嵌套的形式显示在 A 之下。
- 适用场景:适合用于分析关心执行耗时的代码片段。
TIP
子事件必须始终在其父事件结束前结束(即 B 必须在 A 之前结束)
// 基础用法
function handleClick() {
lynx.performance.profileStart('handle-click');
// ... 你的代码 ...
lynx.performance.profileEnd();
}
// 带自定义参数
useEffect(() => {
lynx.performance.profileStart('useEffect', {
args: { count },
});
// ... 你的代码 ...
lynx.performance.profileEnd();
}, [count]);#Instant 事件

- 定义:Instant 事件只有一个时间戳,没有持续时间。
- 适用场景:适用于标记代码中的重要时刻或节点(如状态变更、跨线程/异步边界等)。
function fetchData() {
// 基础用法
lynx.performance.profileMark('fetch-data-begin');
fetch(url).then((res) => {
// 带自定义��参数
lynx.performance.profileMark('fetch-data-end', {
args: { url: 'https://example.com', method: 'GET' },
});
});
}#Flow 事件
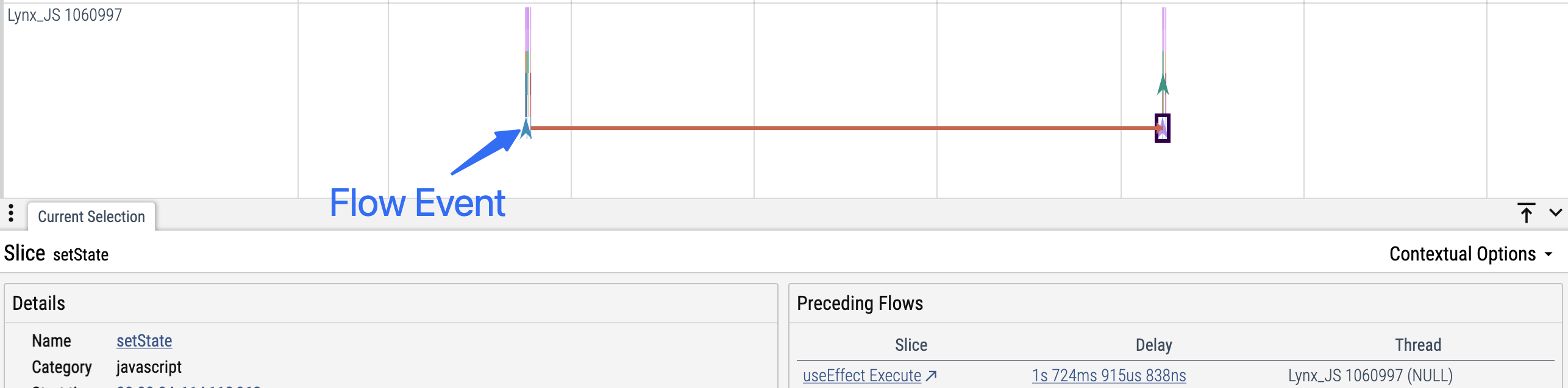
- 描述:Flow 用于将两个(或多个)逻辑相关但可能发生在不同线程或不同时间的事件(Slice 或 Instant)关联起来。
- 可视化:在 Trace UI 中,Flow 会以箭头的形式连接相关事件。当你选中某个事件时,箭头会高亮显示其关联的其他事件。
- 适用场景:Flow 特别适合用于追踪异步任务的生命周期、请求/响应对,或任何跨越多个阶段或上下文的操作。
const flowId = lynx.performance.profileFlowId();
lynx.performance.profileMark('user-action-begin', { flowId });
// ...稍后,在异步回调中
setTimeout(() => {
// ...
lynx.performance.profileMark('user-action-end', { flowId });
}, 1000);#最佳实践
#Begin/End 必须在同一线程且成对出现
- 每个
profileStart必须有一个对应的profileEnd,且这两个调用必须发生在同一线程。 - 不要因为异常或提前 return 而导致
profileEnd未被调用。
#错误示例
function measure() {
lynx.performance.profileStart('measure');
// ...
throw new Error('Error occurred');
// 异常导致 profileEnd 未被调用
lynx.performance.profileEnd();
}
function measureWithFastExit(fastExit) {
lynx.performance.profileStart('measure');
// 直接返回,profileEnd 未被调用
if (fastExit) return;
// ...
lynx.performance.profileEnd();
}
// 跨异步线程调用导致 begin/end 不匹配
lynx.performance.profileStart('background-task');
setTimeout(() => {
// ...
lynx.performance.profileEnd();
}, 1000);#正确示例
function measure(shouldThrow) {
try {
lynx.performance.profileStart('measure');
// ...
throw new Error('Error occurred');
} finally {
// 异常安全,确保 profileEnd 一定被调用
lynx.performance.profileEnd();
}
}
function measureWithFastExit(fastExit) {
lynx.performance.profileStart('measure');
if (fastExit) {
// 提前 return 安全示例
lynx.performance.profileEnd();
return;
}
// ...
lynx.performance.profileEnd();
}
setTimeout(() => {
// 线程安全示例:begin/end 在同一执行上下文
lynx.performance.profileStart('background-task');
// ...
lynx.performance.profileEnd();
}, 0);#不要跨异步边界使用 Slice 事件
- 不要在异步边界(如定时器、回调、
await/Promise)之间使用profileStart/profileEnd。 - Slice 事件要求开始和结束在同一个同步上下文中。
- 如果需要追踪异步边界两侧,请使用 Instant 事件。
#错误示例
// 定时器/回调
lynx.performance.profileStart('async function');
setTimeout(() => {
// ...
lynx.performance.profileEnd();
}, 3000);
// await/promise
lynx.performance.profileStart('await-task');
await someAsyncFunc();
lynx.performance.profileEnd();#正确示例
// 定时器/回调:在回调内部成对使用
setTimeout(() => {
lynx.performance.profileStart('async function');
// ...
lynx.performance.profileEnd();
}, 3000);
// await/promise:使用 Instant 事件
lynx.performance.profileMark('async-task:start');
await someAsyncFunc();
lynx.performance.profileMark('async-task:end');除非另有说明,本项目采用知识共享署名 4.0 国际许可协议进行许可,代码示例采用 Apache License 2.0 许可协议进行许可。