Understanding Layout
Lynx provides:
- Properties such as
width,height,margin, andpaddingare used to describe the size of elements. - The
displayproperty, along with linear layout, flexible box layout, grid layout, and relative layout, are used for laying out elements. - The aligning properties, including
align-items,justify-contentand etc., are used for aligning elements. - The
positionproperty, along withleft,right,top,bottomproperties, are used to position elements. directionand logical properties are used to support the internationalization of layouts.
For the layout properties supported by Lynx with the same name in the Web, the behavior of these properties will be consistent with those in the Web.
However, there is a difference in the design concept between Lynx layout and Web layout: Web layout is primarily text-based. While Lynx layout is based on elements (<view>, <text>, <image>, etc.). In other words, elements in Lynx are all block-level elements.
The following tutorial will show you how to complete the layout of elements in Lynx.
Sizing the Elements
You can use width, height, max-width, min-width, max-height, min-height, margin, padding, and border-width to describe the size and box model of an element. These properties support various length units such as px, %, vh and etc. Additionally, width and height support max-content and fit-content for sizing elements according to their content.

box-sizing is border-box by default and Lynx does not exhibit the behavior of margin collapsing.
By default, the size properties of Lynx, such as width, height, and max-width, describe the size of the border box. This is inconsistent with the default behavior of the Web.
Lynx does not exhibit the behavior of margin collapsing as in the Web.
Layout the Elements
The <view> element can be used for laying out child elements, and by setting the display property on the <view> element, you can control the way it lays out its child elements. The display property supports five values: linear, flex, grid, relative and none.
Linear Layout
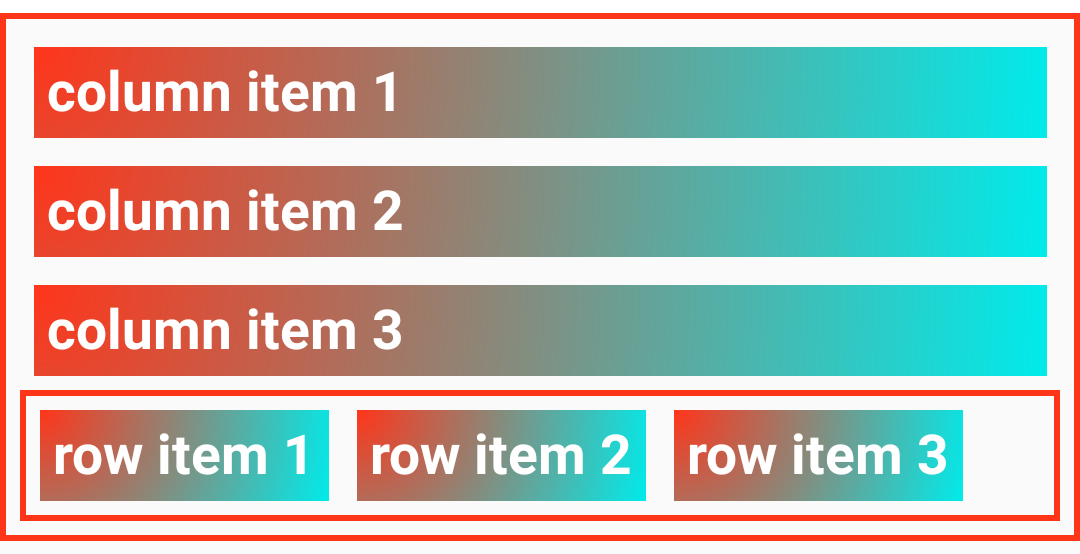
If you want to simply arrange the elements in order, you can set the display property to linear and use Lynx's default layout, which is the linear layout. The Linear layout (inspired by Android's Linear Layout) can arrange the elements in order according to the direction you declare.
Flexible Box Layout
If you need to make the size of child elements adapt to the space of the parent element (such as expanding child elements to fill the unused space or shrinking child elements to avoid overflow), you can set the display property to flex and use the flexible box layout. The flexible box layout in Lynx is consistent with the one in Web.

Grid Layout
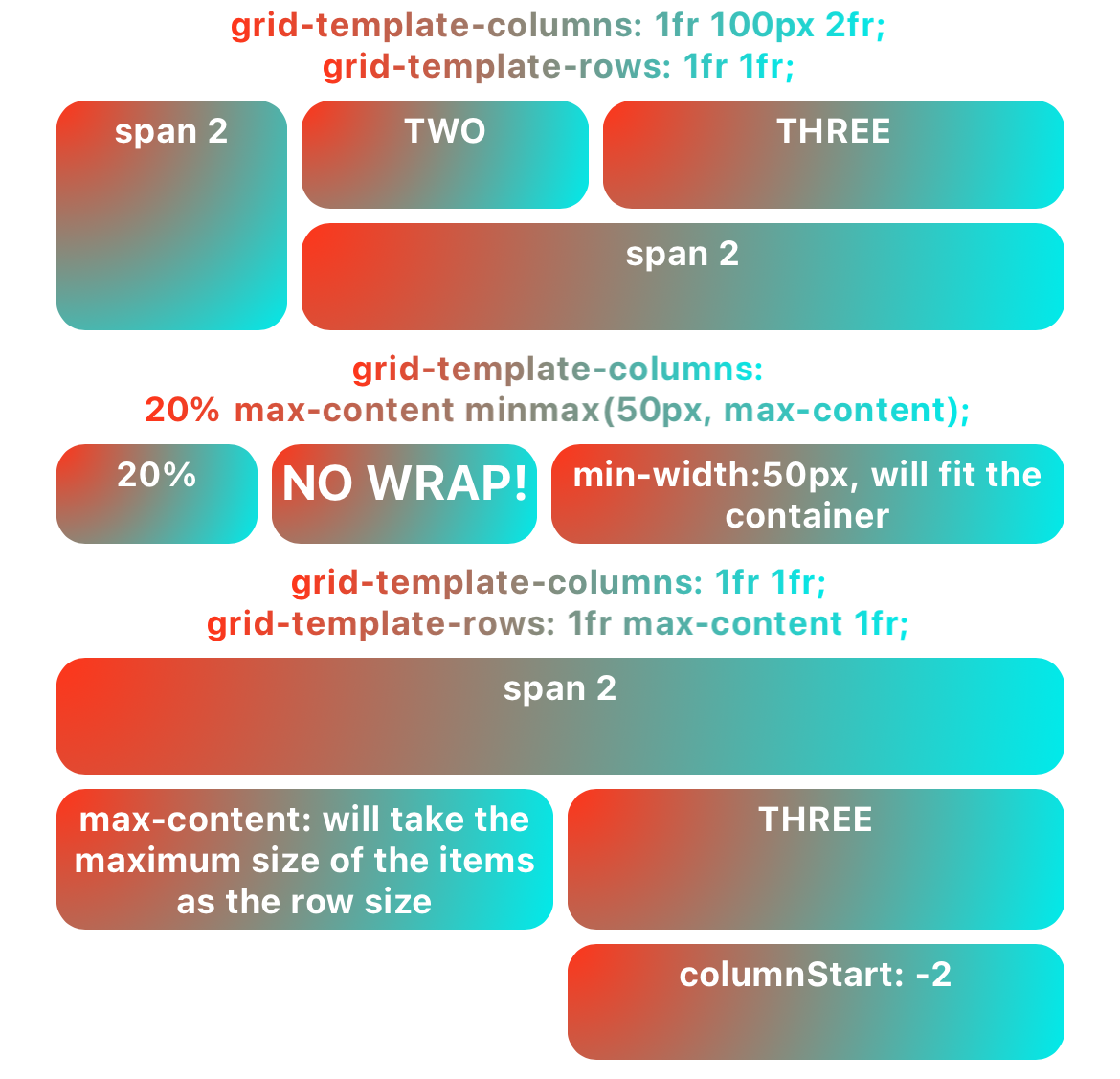
If you want to arrange multiple elements alternately in both vertical and horizontal directions to form a two-dimensional layout, you can set the display property to grid and use the grid layout, a layout in the Web that can divide the space into a two-dimensional grid and place elements in the specified rows and columns. Lynx supports a subset of its features.
Relative Layout
If you want to describe the layout through the relative position relationship between elements, you can set the display property to relative and use the relative layout. The relative layout(inspired by Android's Relative Layout) can declare the layout by describing the position relationship between elements (for example, one element is located to the left of another element).

Text and Inline Layout
In Lynx, text cannot be directly inserted into the <view> element, and the display property of Lynx does not support the values of inline and block. The <text> element can complete text display and the inline layout of elements. For details, please refer to Text Typography.
Aligning the Elements
You can align the elements laid out by a <view> with align-items, align-self, justify-content, align-content, justify-items and justify-self properties.

Offseting and Absolute Positioning
You can offset the elements with top, left, bottom, and right properties. And you can make elements absolutely positioned with position property.

Internationalization
You can use the direction property and logical properties to make your page support both languages written from left to right (such as Chinese) and languages written from right to left (such as Arabic).
logical properties refer to a series of properties like XX-inline-start and XX-inline-end (such as inset-inline-start).
Please refer to CSS
Inheritance,
using enableCSSInheritance to enable direction to be inheritable, and
using logical properties depends on the direction value.
