选择器
CSS 选择器规定了 CSS 规则会被应用到哪些元件上。严格来说,CSS 选择器是一个涵盖选择器、组合器、伪元素和伪类的总称。
选择器(Selectors)
类型选择器(Type selector)
CSS 类型选择器通过节点名称匹配元件。换句话说,它选择一个文件中所有给定类型的元件。
语法
使用示例
通过 page 来选择根节点
与 Web 不同,Lynx 里使用 page 来选择根节点,而非 body。
类选择器(Class selector)
按照给定的 class 属性的值,选择所有匹配的元件。
语法
使用示例
多类选择器 (Multiple Class Selectors)
使用多个类名来选择元件,通过将多个类名连在一起的方法来指定一个元件必须同时包含这些类
语法
使用示例
ID 选择器(ID selector)
按照 id 属性选择一个与之匹配的元件。需要注意的是,一个文档中,每个 ID 属性都应当是唯一的。
语法
通配符选择器(Universal selector)
星号(*)就是一个通配选择器,它可以匹配任意类型的元件。
语法
组合器 (Combinator)
后代选择器 (descendant Combinator)
通过空格组合了两个选择器,如果第二个选择器匹配的元件具有与第一个选择器匹配的祖先(父母,父母的父母,父母的父母的父母等)元件,则它们将被选择。
语法
使用示例
子代组合器 (Child Combinator)
子组合器(>)被放在两个 CSS 选择器之间。它只匹配那些被第二个选择器匹配的元件,这些元件是被第一个选择器匹配的元件的直接子元件。
语法
使用示例
后续兄弟组合器 (Subsequent-sibling Combinator)
后续兄弟选择器(~)将两个选择器分开,并匹配第二个选择器的所有迭代元件,位置无须紧邻于第一个元件,只须有相同的父级元件。
语法
使用示例
紧邻兄弟组合器 (Next-sibling Combinator)
接续兄弟选择器(+)介于两个选择器之间,当第二个元件紧跟在第一个元件之后,并且两个元件都是属于同一个父元件的子元件,则第二个元件将被选中。
语法
使用示例
选择器列表 (Selector list)
CSS 选择器列表(,)选择所有匹配的节点。选择器列表是以逗号分隔的多个选择器所组成的列表。
语法
使用示例
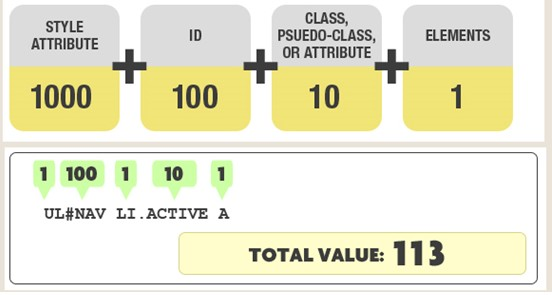
伪类 (Pseudo-class)
: 伪类是选择器的一种,它用于选择处于特定状态的元件。
支持:
:not():root:active
:not()
用来匹配不符合条件的元件,用法对齐 W3C :not()
:root
与 page 选择器类似,用来匹配根节点, 用法对齐 W3C :root
:active
节点被用户按压后,会被激活选中,松开手指则不被激活,用法对齐 W3C :active
使用示例
伪元素 (Pseudo-element)
伪元素是一个附加至选择器末的关键词,允许你对被选择元件的特定部分修改样式。目前支持 ::selection 伪元�素。
::selection
::selection 用于设置文本选中后高亮的样式,支持的属性包括 background-color,用于设置高亮背景色,-x-handle-size 和 -x-handle-color 属性用于设置浮标样式。
使用示例
常见问题
CSS 权重不支持 !important
需要特别注意的是,Lynx 不支持 !important 这个权重设置。除此之外,Lynx 遵循和 Web 一致的权重计算方式来定义样式规则的优先级次序。权重的基本计算逻辑如下: