background-image
Introduction
The background-image CSS property sets one or more background images on an element.
The background images are drawn on stacking context layers on top of each other. The first layer specified is drawn as if it is closest to the user.
The border of the element are then drawn on top of them, and the background-color is drawn beneath them. How the images are drawn relative to the box and its borders is defined by the background-clip and background-origin CSS properties.
Examples
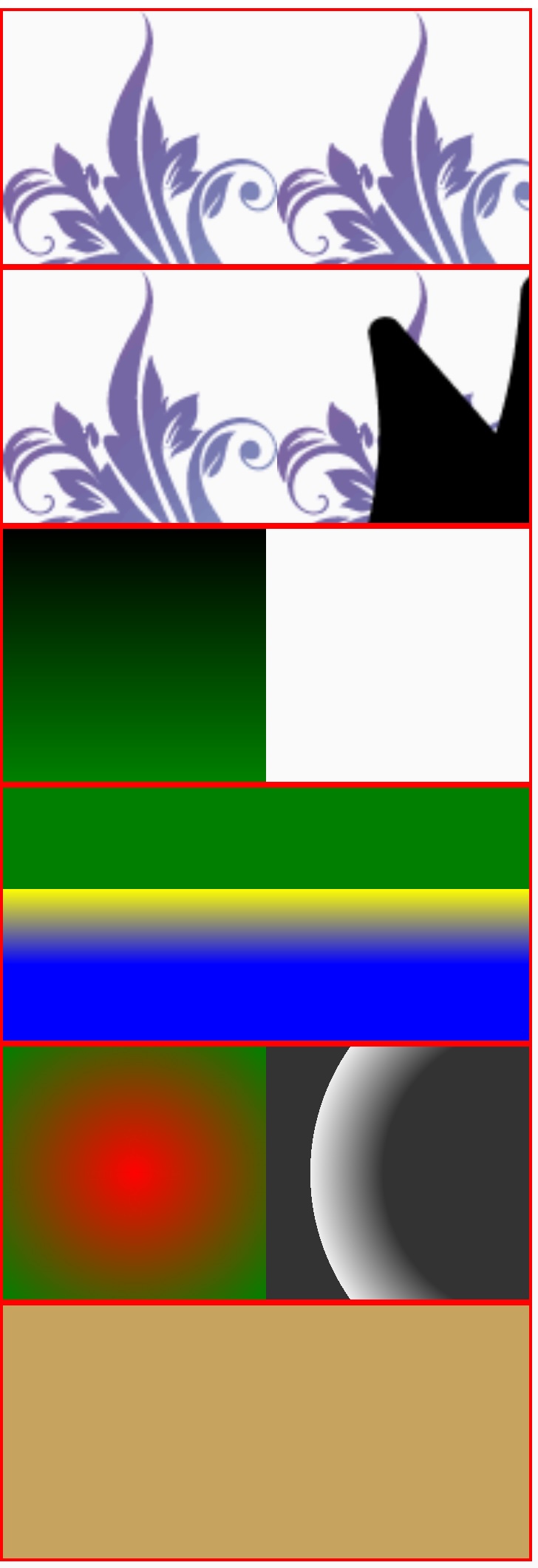
Syntax
Values
Each background image is specified either as the keyword none or as an <image> value.
-
noneIs a keyword denoting the absence of images. -
<image>Is an<image>denoting the image to display. There can be several of them, separated by commas. The supported image formats for background-image are the same as those for image, including jpg, png, gif, webp, etc. Refer to Supported Image Formats
Events
| Name | Type | Essential | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| bindbgload | function | NO | Loading succeed |
| bindbgerror | function | NO | Loading failed |
Related properties of view
| Name | Type | Default | Example | Essential | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Android skip-redirection | boolean | false | true | NO | It only needs to be set when the background-image uses <url()> and is a CDN image. When set to true, the logic of container redirection can be skipped to optimize the related time-consuming |
Formal definition
| Initial value | none |
| Applies to | all elements |
| Inherited | no |
| Animatable | no |
Formal Syntax
Difference between web
-
<image>Only support<url()>and<gradient>. -
<gradient>Supportlinear-gradient,radial-gradient, andconic-gradient(since version 3.6). -
<linear-color-stop>Not supportlinear-color-hintNot support
color-interpolation-methodNot support
<length>value for position
Compatibility
LCD tables only load in the browser