z-index
Introduction
The z-index CSS property sets the z-order of an element and its descendants or flex items. Overlapping elements with a larger z-index cover those with a smaller one.
If we want to generate stacking context, you can add z-index: 0 to an element. For example, make children follow the scroll by adding z-index: 0 to the scroll-view
It is not recommended to use z-index in the direct children of list. This may affect the reuse of list. If you use z-index in the list item, the item should be a stacking context.
Examples
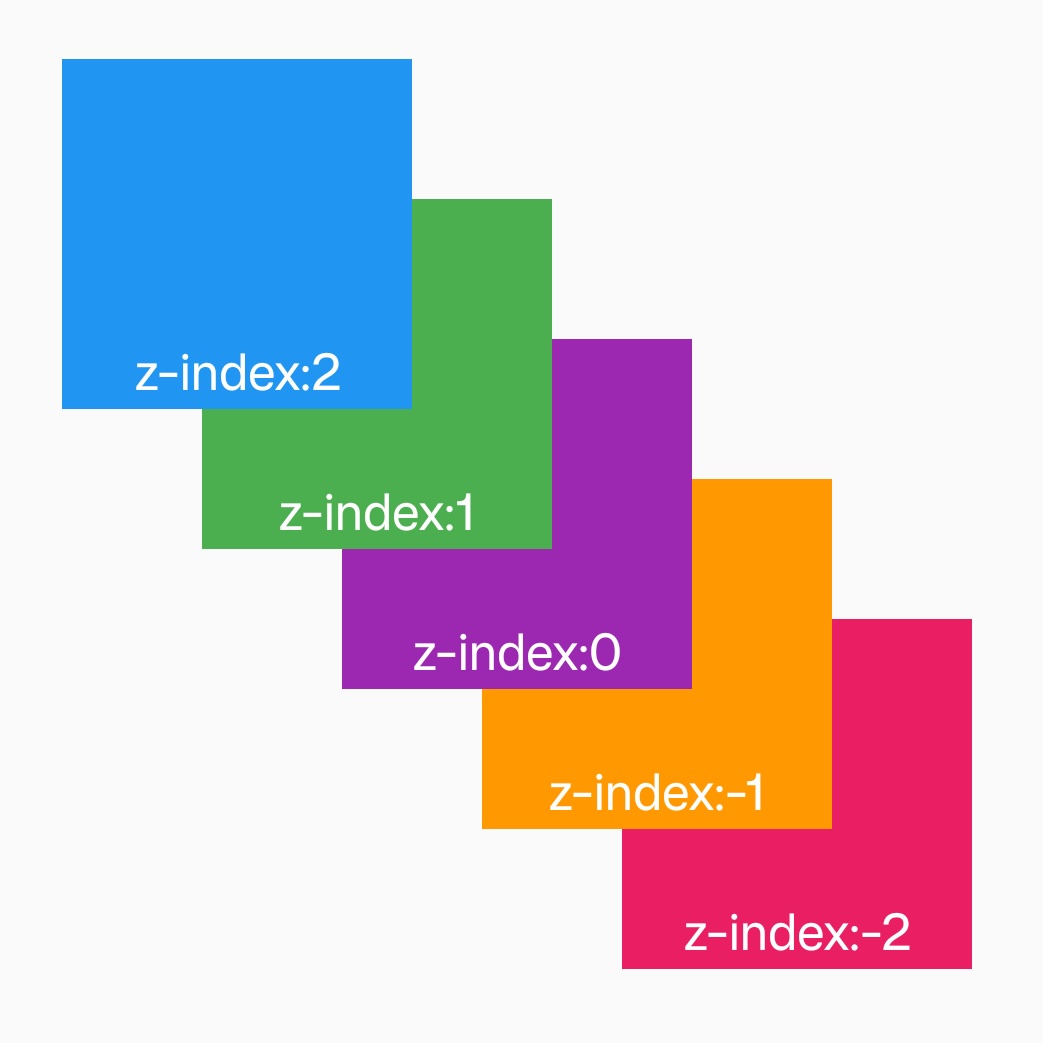
Syntax
Values
-
<number>This integer is the stack level of the generated box in the current stacking context. -
Default value auto
Formal definition
| Initial value | empty value |
| Applies to | all elements |
| Inherited | no |
| Animatable | no |
Formal syntax
Difference between web
The default value of web is auto. Lynx determines whether it is a stacking context by setting z-index property.
Compatibility
LCD tables only load in the browser