<scroll-view>
Basic scrolling component supporting both horizontal and vertical scrolling. When its content area is larger than its visible area, it allows users to scroll to reveal more content.
Usage
Horizontal and Vertical Scrolling
<scroll-view> supports both horizontal and vertical scrolling, implemented through the scroll-orientation properties.
<scroll-view> always uses the linear layout, and the layout direction is determined by the scroll-orientation attributes.
Scroll Events
Use event callbacks such as bindscroll, bindscrolltoupper, and bindscrolltolower to monitor changes in scroll progress.
Sticky Capability
As a child node of <scroll-view>, you can set the sticky attribute making the child node remain at a certain distance from the top of the <scroll-view> and not continue scrolling with the content.
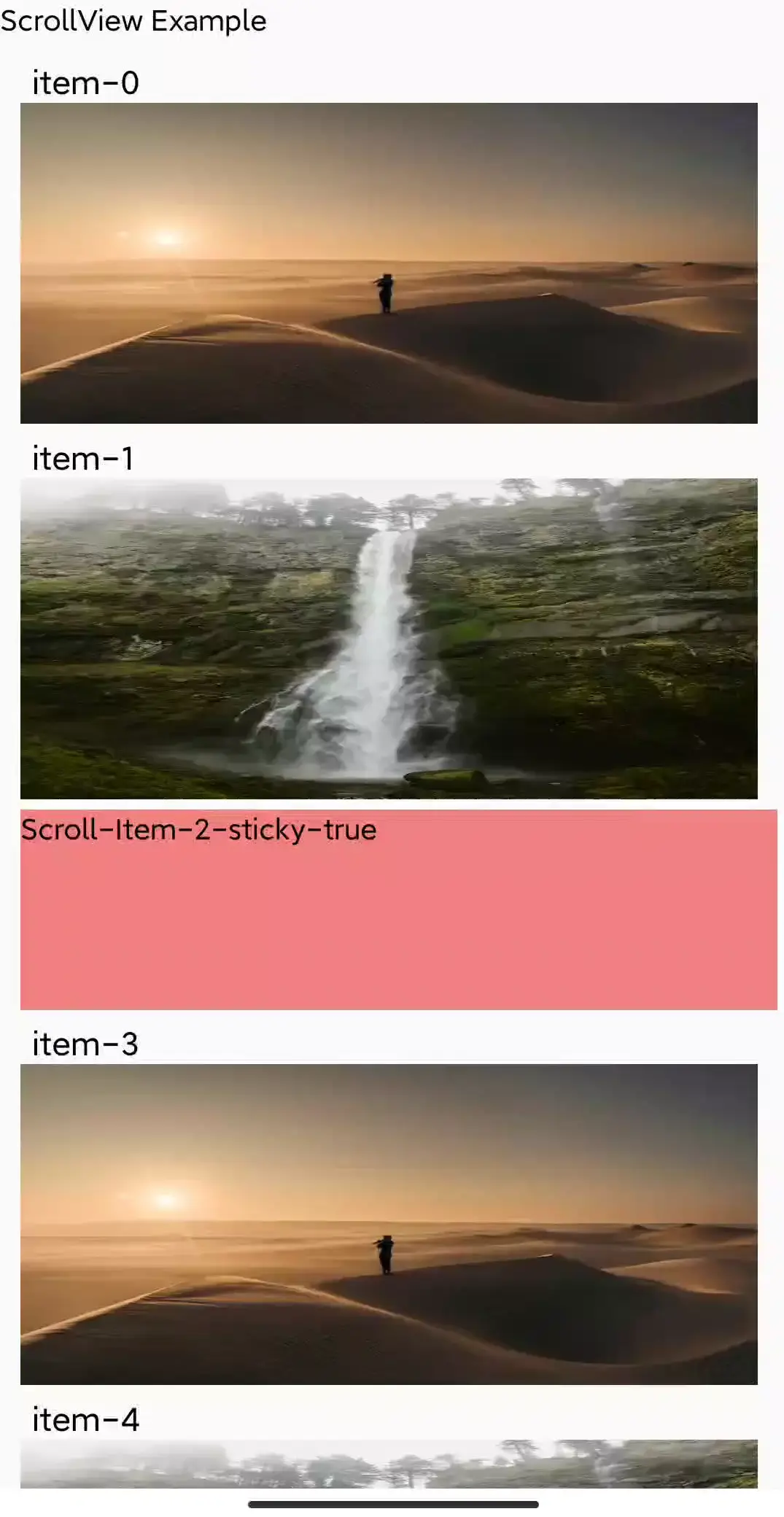
sticky can only be set for direct child nodes of <scroll-view>. On Android, you need to add the flatten={false} attribute to sticky nodes.
The direct child nodes of <scroll-view> only support linear and sticky. If you need more complex layouts, such as child nodes adapting to expand, it is recommended to provide a single child view to the <scroll-view> and implement more robust CSS capabilities within that single child node.
Attributes
bounces
iOS
Clay
Harmony
1.4
Enable bounce effect
enable-scroll
Android
iOS
Clay
Harmony
1.4
Enable dragging
initial-scroll-offset
Android
iOS
Clay
Harmony
2.17
Initial scroll position, only effective once, in PX
initial-scroll-to-index
Android
iOS
Clay
Harmony
2.17
Scroll to specified child node on first screen, only effective once. All direct child nodes must be flatten=false.
lower-threshold
Android
iOS
Clay
Harmony
1.4
Set upper threshold to bindscrolltoupper event.
scroll-bar-enable
iOS
Clay
Harmony
1.4
Enable scrollbar
scroll-orientation
Android
iOS
Clay
Harmony
3.0
Replacement of scroll-x and scroll-y
upper-threshold
Android
iOS
Clay
Harmony
1.4
Set upper threshold to bindscrolltoupper event.
Events
Frontend can bind corresponding event callbacks to listen for runtime behaviors of the element, as shown below.
bindcontentsizechanged
Android
iOS
Harmony
1.6
This event is triggered when the scrollview's content size changed.
bindscroll
Android
iOS
Clay
Harmony
1.4
This event is triggered when the scrollview is scrolling.
bindscrollend
Android
iOS
Clay
Harmony
1.6
This event is triggered when the scrollview's scroll ended.
bindscrolltolower
Android
iOS
Harmony
1.4
This event is triggered when the lower/right edge of the scrolling area intersects with the visible area defined by the lowerThreshold.
bindscrolltoupper
Android
iOS
Harmony
1.4
This event is triggered when the upper/left edge of the scrolling area intersects with the visible area defined by the upperThreshold.
Methods
Frontend can invoke component methods via the SelectorQuery API.
autoScroll
Android
iOS
Clay
Harmony
Automatic scrolling
getScrollInfo
Android
iOS
Clay
Harmony
Get scroll info
scrollBy
Android
iOS
Clay
Harmony
Scroll by specified offset
scrollTo
Android
iOS
Clay
Harmony
Scroll to specified position
Performance Optimization Suggestions
<scroll-view> creates all of its child nodes at once, potentially causing severe first-screen load times. Use exposure events to drive it to create only visible child nodes.
<scroll-view> lacks any reuse mechanism. If content is too extensive, it may consume an exceptionally large amount of memory, possibly causing OOM and other stability problems.
For data exceeding three screens, use <list> to optimize performance, or simulate <VisualizedList> logic based on exposure events.
Compatibility
LCD tables only load in the browser