LoadBundleEntry
LoadBundle refers to the initial frame rendering pipeline triggered by LynxView loading and executing the TemplateBundle. LoadBundleEntry is used to record the performance data of this rendering pipeline and inherits from PipelineEntry.
The LoadBundle process flowchart is as follows:
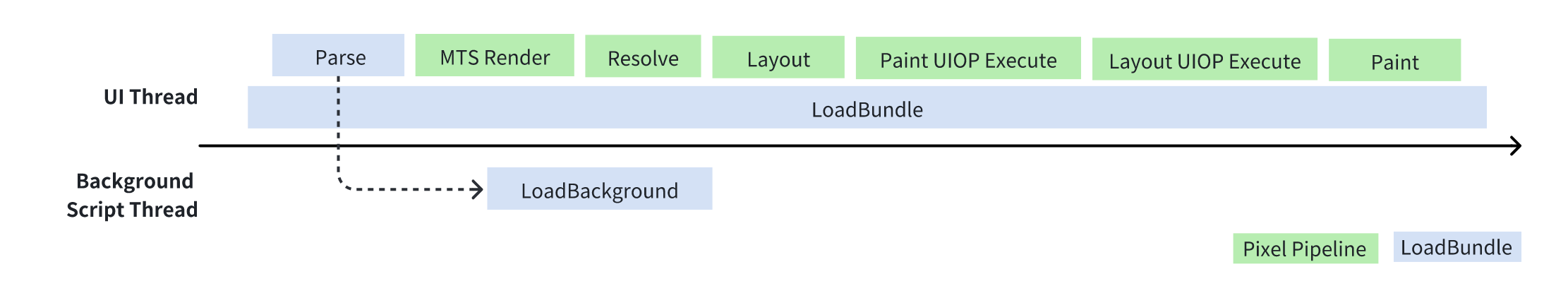
If you fail to receive LoadBundleEntry, it may be due to the following reasons:
1. Rendering not triggered
The rendering pipeline is not executed, typically because:
- LynxView container state issues: Width/Height is 0, not in the viewport, or not added to the window.
- Business logic renders no content: For example, in ReactLynx, the component's
render()function returnsnullbecause data is not ready.
2. Listener registered too late
LoadBundleEntry is triggered only once upon completion of initial rendering. It is recommended to register the listener as early as possible:
- Register in
constructorfor class components. - register in
useMemofor functional components.
Example
This example demonstrates how to obtain a LoadBundleEntry.
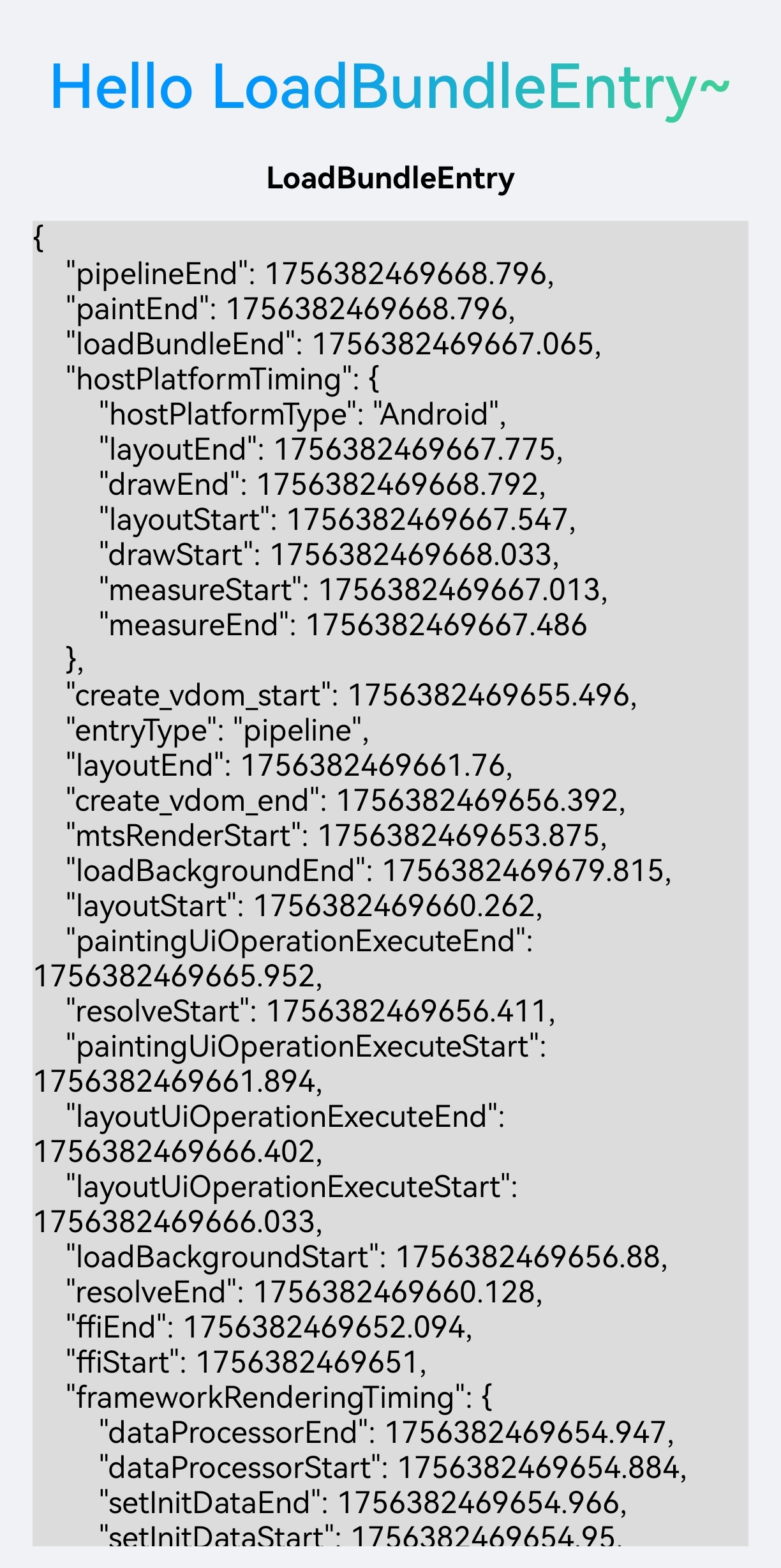
Instance properties
entryType
The type of the performance event; the value for all instances of this class is fixed as pipeline.
name
The specific name of the performance event; the value for all instances of this class is fixed as loadBundle.
identifier
A marker for a particular rendering pipeline; the value for all instances of this class is fixed as an empty string.
loadBundleStart
The timestamp for the start of loading and executing the TemplateBundle. This timestamp is represented as a floating-point Unix timestamp (in milliseconds) with three decimal places. For example: 1739594612307.429.
loadBundleEnd
The timestamp for the end of loading and executing the TemplateBundle. This timestamp is represented as a floating-point Unix timestamp (in milliseconds) with three decimal places. For example: 1739594612307.429.
parseStart
The timestamp for the start of parsing the TemplateBundle. This timestamp is represented as a floating-point Unix timestamp (in milliseconds) with three decimal places. For example: 1739594612307.429.
parseEnd
The timestamp for the end of parsing the TemplateBundle. This timestamp is represented as a floating-point Unix timestamp (in milliseconds) with three decimal places. For example: 1739594612307.429.
loadBackgroundStart
The timestamp for the start of loading and executing the background thread scripts in the TemplateBundle. This timestamp is represented as a floating-point Unix timestamp (in milliseconds) with three decimal places. For example: 1739594612307.429.
loadBackgroundEnd
The timestamp for the end of loading and executing the background thread scripts in the TemplateBundle. This timestamp is represented as a floating-point Unix timestamp (in milliseconds) with three decimal places. For example: 1739594612307.429.
pipelineStart
The timestamp for the start of the rendering pipeline. This timestamp is represented as a floating-point Unix timestamp (in milliseconds) with three decimal places. For example: 1739594612307.429.
pipelineEnd
The timestamp for the end of the rendering pipeline. This timestamp is represented as a floating-point Unix timestamp (in milliseconds) with three decimal places. For example: 1739594612307.429.
mtsRenderStart
The timestamp for the start of executing the main thread scripts to build the Element Tree. This timestamp is represented as a floating-point Unix timestamp (in milliseconds) with three decimal places. For example: 1739594612307.429.
mtsRenderEnd
The timestamp for the end of executing the main thread scripts to build the Element Tree. This timestamp is represented as a floating-point Unix timestamp (in milliseconds) with three decimal places. For example: 1739594612307.429.
resolveStart
The timestamp for the start of calculating Element styles. This timestamp is represented as a floating-point Unix timestamp (in milliseconds) with three decimal places. For example: 1739594612307.429.
resolveEnd
The timestamp for the end of calculating Element styles. This timestamp is represented as a floating-point Unix timestamp (in milliseconds) with three decimal places. For example: 1739594612307.429.
layoutStart
The timestamp for the start of layout calculations. This timestamp is represented as a floating-point Unix timestamp (in milliseconds) with three decimal places. For example: 1739594612307.429.
layoutEnd
The timestamp for the end of layout calculations. This timestamp is represented as a floating-point Unix timestamp (in milliseconds) with three decimal places. For example: 1739594612307.429.
paintingUiOperationExecuteStart
The timestamp for the start of executing UI operations related to painting. This timestamp is represented as a floating-point Unix timestamp (in milliseconds) with three decimal places. For example: 1739594612307.429.
paintingUiOperationExecuteEnd
The timestamp for the end of executing UI operations related to painting. This timestamp is represented as a floating-point Unix timestamp (in milliseconds) with three decimal places. For example: 1739594612307.429.
layoutUiOperationExecuteStart
The timestamp for the start of executing UI operations related to layout. This timestamp is represented as a floating-point Unix timestamp (in milliseconds) with three decimal places. For example: 1739594612307.429.
layoutUiOperationExecuteEnd
The timestamp for the end of executing UI operations related to layout. This timestamp is represented as a floating-point Unix timestamp (in milliseconds) with three decimal places. For example: 1739594612307.429.
paintEnd
The timestamp for the end of completing the final pixelation based on UI and UITree. This timestamp is represented as a floating-point Unix timestamp (in milliseconds) with three decimal places. For example: 1739594612307.429.
frameworkPipelineTiming
Performance data for key stages in Framework Rendering. The type is FrameworkPipelineTiming.
hostPlatformTiming
Performance data for platform-specific key stages in Lynx Pipeline, with type AndroidHostPlatformTiming | HarmonyHostPlatformTiming | IOSHostPlatformTiming.
Compatibility
LCD tables only load in the browser